Understanding Meniscus Tear Recovery

Recovering from a meniscus tear can be a challenging process, but understanding the different types of tears, the potential symptoms, and the available treatment options can help you navigate your recovery journey effectively. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of meniscus tear recovery, empowering you to make informed decisions about your treatment and rehabilitation.
Types of Meniscus Tears and Their Causes
The meniscus, a C-shaped piece of cartilage in the knee, acts as a shock absorber and helps stabilize the joint. Meniscus tears can occur due to various factors, including:
- Sudden twisting or pivoting movements, especially during sports or physical activities, can cause the meniscus to tear.
- Direct impact to the knee, such as a fall or a blow, can also lead to a meniscus tear.
- Degenerative changes in the meniscus, often associated with aging, can weaken the cartilage and make it more susceptible to tearing.
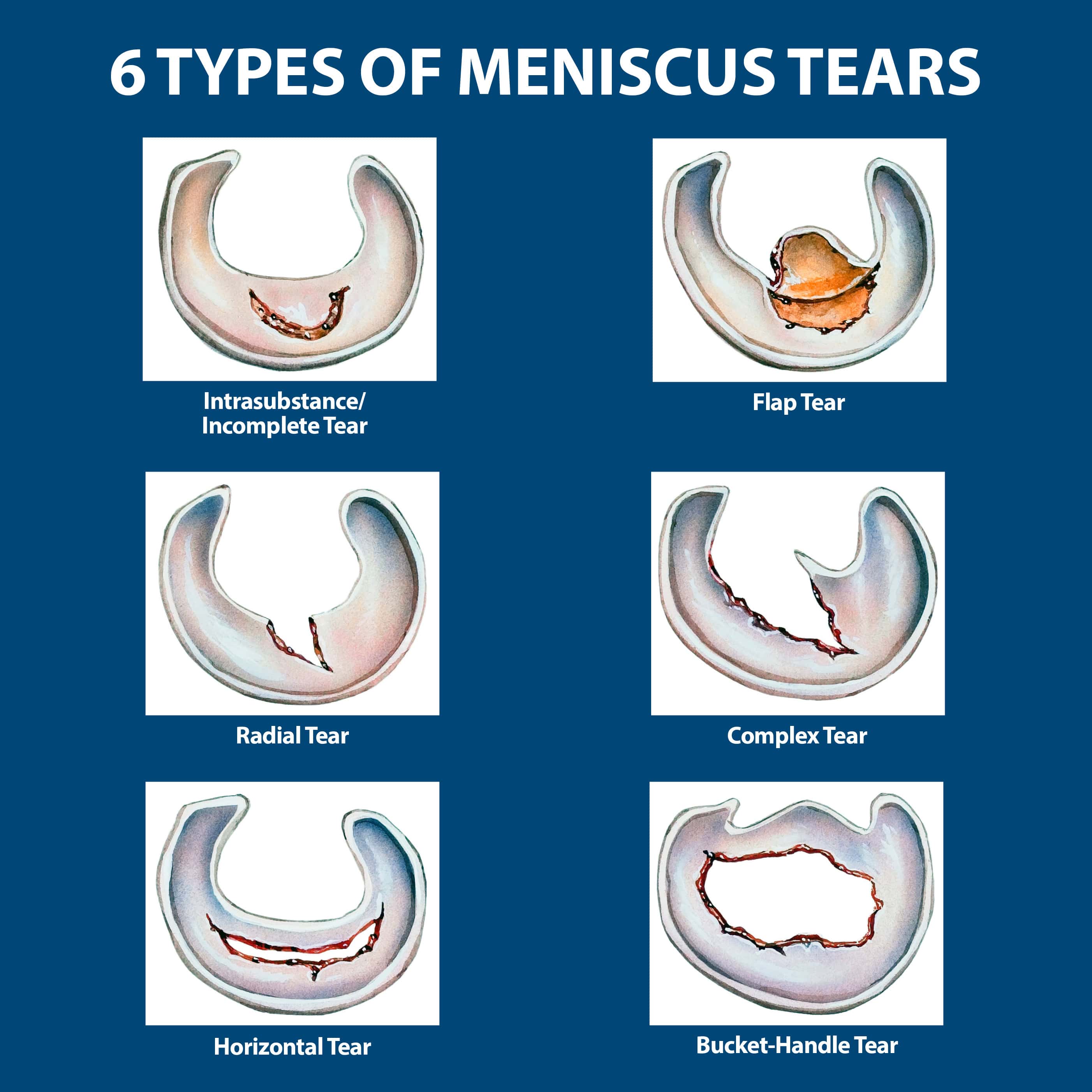
There are different types of meniscus tears, categorized based on their location and severity:
- Horizontal tear: This type of tear occurs across the width of the meniscus.
- Vertical tear: This tear runs from the top to the bottom of the meniscus.
- Radial tear: This tear is shaped like a spoke, extending from the outer edge of the meniscus towards the center.
- Bucket-handle tear: This tear is a large, flap-like tear that can get trapped within the knee joint.
Symptoms of a Meniscus Tear
The symptoms of a meniscus tear can vary depending on the severity of the tear and the individual’s overall health. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain, especially when bending or twisting the knee.
- Swelling around the knee joint.
- Stiffness and difficulty moving the knee.
- Clicking or popping sensation in the knee.
- Locking or catching of the knee, making it difficult to fully straighten the leg.
- Feeling of instability or giving way in the knee.
Meniscus Tear Recovery Timeline
The recovery timeline for a meniscus tear can vary significantly depending on the type and severity of the tear, as well as the chosen treatment method. In general, non-surgical treatment for a meniscus tear can take several weeks to months for full recovery, while surgical treatment may require a longer recovery period, often several months.
Treatment Options for Meniscus Tears
The treatment for a meniscus tear will depend on several factors, including the individual’s age, activity level, the type and severity of the tear, and the presence of other knee conditions.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Non-surgical treatment options are typically recommended for minor meniscus tears or for individuals who are not very active. These options may include:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that put stress on the knee can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, can help reduce swelling.
- Compression: Wrapping the knee with a compression bandage can help reduce swelling and provide support.
- Elevation: Keeping the knee elevated above the heart can also help reduce swelling.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve flexibility can help restore function and prevent further injury.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment is typically reserved for more severe meniscus tears or for individuals who do not respond to non-surgical treatment. There are two main types of surgical procedures for meniscus tears:
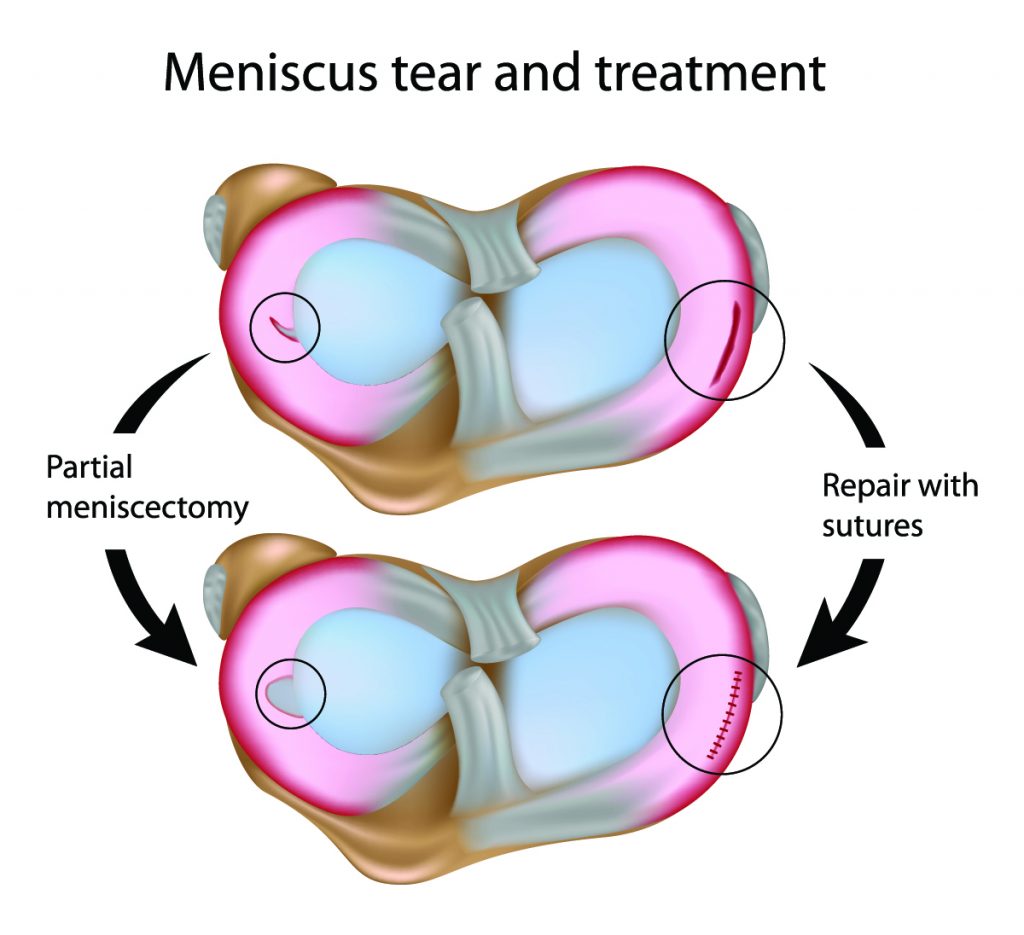
- Meniscectomy: This procedure involves removing the torn portion of the meniscus. It is often performed for tears that are not repairable or for individuals who are not candidates for repair.
- Meniscus repair: This procedure involves stitching the torn meniscus back together. It is typically performed for tears that are repairable and for individuals who are younger and more active.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Meniscus Tears
Many meniscus tears can be effectively treated without surgery, allowing individuals to regain function and reduce pain. These non-surgical options focus on managing pain, reducing inflammation, and promoting healing.
Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE)
RICE is a common first-line treatment for meniscus tears. It helps reduce pain, inflammation, and swelling, promoting healing.
- Rest: Avoid activities that put stress on the injured knee. This allows the torn meniscus to heal and prevents further damage.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the injured area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. This helps reduce inflammation and pain.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage or wrap to help reduce swelling and provide support to the knee.
- Elevation: Keep the injured leg elevated above the heart, especially during the first few days after the injury. This helps reduce swelling by promoting fluid drainage.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in meniscus tear recovery. It helps strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improve flexibility, and restore range of motion.
- Exercises: Physical therapists design a personalized exercise program that includes strengthening, stretching, and range-of-motion exercises. This helps improve knee stability and function.
- Manual Therapy: Physical therapists may use manual therapy techniques, such as massage and mobilization, to address any stiffness or muscle imbalances.
- Proprioceptive Training: This type of training helps improve balance and coordination, which are essential for knee stability and preventing future injuries.
Medications
Medications can help manage pain and inflammation associated with meniscus tears.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: In some cases, stronger anti-inflammatory medications, such as corticosteroids, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation. These are often administered as injections directly into the knee joint.
Bracing and Support Devices
Braces and support devices can provide stability and reduce stress on the injured knee, promoting healing and preventing further injury.
- Knee Braces: These can be worn during activities to provide support and limit movement, allowing the meniscus to heal. Braces come in various types, including hinged braces for greater stability and unhinged braces for less restriction.
- Patellar Tendon Straps: These straps help to stabilize the kneecap and reduce stress on the meniscus.
Surgical Treatment Options for Meniscus Tears
If conservative treatments like rest, medication, and physical therapy fail to alleviate symptoms or if the meniscus tear is severe, surgery may be recommended. Surgical options aim to either repair or remove the torn meniscus.
Meniscus Repair, Meniscus tear recovery
Meniscus repair is a surgical procedure that involves stitching the torn meniscus back together. This procedure is typically recommended for tears in the outer portion of the meniscus, which has a better blood supply and therefore a higher chance of healing.
The surgeon will use sutures, anchors, or other devices to secure the torn edges of the meniscus. The goal of this procedure is to restore the meniscus’s function and prevent further deterioration of the knee joint.
Meniscectomy
Meniscectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing the torn portion of the meniscus. This procedure is often recommended for tears in the inner portion of the meniscus, which has a poor blood supply and is less likely to heal.
Meniscectomy can be performed using arthroscopic surgery, a minimally invasive technique that uses small incisions and a camera to visualize the knee joint. During the procedure, the surgeon will remove the damaged portion of the meniscus using specialized instruments.
Risks and Benefits of Meniscus Surgery
Both meniscus repair and meniscectomy have potential risks and benefits.
Risks
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding can occur during or after surgery.
- Blood clots: Blood clots can form in the legs after surgery, potentially leading to a pulmonary embolism.
- Stiffness: The knee joint may become stiff after surgery, requiring extensive rehabilitation.
- Damage to surrounding structures: There is a risk of damage to other structures in the knee joint, such as ligaments, tendons, or nerves.
- Re-tear: The repaired meniscus may tear again.
- Arthritis: Long-term, meniscectomy may increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis in the knee joint.
Benefits
- Pain relief: Surgery can effectively relieve pain and improve knee function.
- Improved stability: Meniscus repair can help stabilize the knee joint.
- Delayed onset of arthritis: Meniscus repair may help delay the onset of osteoarthritis.
Recovery Process
The recovery process after meniscus surgery varies depending on the type of surgery performed and the individual’s overall health.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is crucial for a successful recovery after meniscus surgery. Physical therapy will focus on regaining range of motion, strength, and stability in the knee joint.
Rehabilitation exercises may include:
- Range of motion exercises
- Strengthening exercises
- Balance exercises
- Proprioceptive exercises
The duration of rehabilitation can range from several weeks to several months.
Long-Term Outcomes
The long-term outcomes of meniscus surgery depend on factors such as the age of the patient, the severity of the tear, and the type of surgery performed.
Potential Complications
Potential complications after meniscus surgery include:
- Re-tear: The repaired meniscus may tear again.
- Arthritis: Long-term, meniscectomy may increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis in the knee joint.
- Stiffness: The knee joint may become stiff after surgery, requiring extensive rehabilitation.
- Pain: Some patients may experience persistent pain after surgery.
Meniscus tear recovery – Recovering from a meniscus tear can be a tough journey, but with the right support and dedication, you can get back on your feet. Just ask Jahmyr Gibbs, the talented running back for the Detroit Lions, who recently made a strong comeback after his own injury.
Jahmyr Gibbs is a testament to the power of perseverance and a reminder that even with setbacks, achieving your goals is possible. So, whether you’re an athlete or just looking to get back to your daily activities, remember that meniscus tear recovery is achievable with the right approach.
Recovering from a meniscus tear can be a long and challenging process, but it’s crucial to stay informed and follow your doctor’s instructions. While a meniscus tear is a common knee injury, it’s important to understand that other conditions, like a gibbs injury , can also cause knee pain and discomfort.
Understanding the nuances of these different injuries is key to getting the right treatment and achieving a full recovery.
